P11D – Complete Guide to HMRC Employee Benefits, Expenses, Deadlines & How to Report Benefits in Kind
What Is the P11D Form?
The P11D is HMRC’s official form used by employers to report Benefits in Kind (BiKs) provided to employees and directors. These are non-cash benefits that have a taxable value, such as:
-
Company cars
-
Health insurance
-
Interest-free or low-interest loans
-
Gym memberships
-
Private medical care
-
Travel and subsistence benefits
-
Fuel cards
-
Mobile phones (if not exempt)
-
Relocation payments
-
Assets provided for personal use
The P11D form must be completed for each employee or director who receives taxable benefits that are not included in the payroll.
The P11D works together with:
-
P11D(b) – Employer declaration form
-
Class 1A National Insurance contributions (NIC)
-
PAYE coding notices
Looking for assistance with Payroll Services? Our Employee Payroll Management Services ensure accurate reporting for employer and employee.
Why the P11D Matters
Incorrect or late P11D submissions can lead to:
-
HMRC penalties
-
Incorrect tax codes
-
Unexpected tax bills for employees
-
Additional NICs for employers
-
Compliance checks or PAYE audits
-
Delays in payroll processing
This guide explains everything employers and employees must know about P11Ds, how to complete them, and how Audit Consulting Group can help.
Who Must Submit a P11D?
A P11D must be submitted if an employer provides any taxable benefits to:
– Employees earning more than £8,500 a year (virtually everyone today)
– Directors
– Employees with company benefits through salary sacrifice
– Anyone receiving non-payrolled benefits
A P11D must be completed even if only one benefit was provided and only for part of the year.
You must NOT submit a P11D if:
-
All benefits are processed through payroll (“payrolling benefits”)
-
No benefits were provided
-
Objectively exempt items apply (e.g., business travel, employer mobile phones)
What the P11D Covers
Every P11D is divided into categories, including:
1. Cars and car fuel
Company cars and fuel benefits have specific HMRC calculations.
2. Vans and van fuel
Vans used privately also create a benefit.
3. Private medical insurance
Most policies are taxable.
4. Interest-free and low-interest loans
These trigger a “beneficial loan” charge if over £10,000.
5. Assets provided for personal use
Includes laptops, tools, equipment, property.
6. Living accommodation
Company-provided housing is a taxable benefit.
7. Mileage and travel costs
Expenses paid above HMRC approved rates must be reported.
8. Relocation and moving expenses
Amounts over £8,000 are taxable.
9. Other benefits
Gym memberships, subscriptions, vouchers, tuition, etc.
P11D vs P11D(b): What’s the Difference?
P11D – Employee Level Report
For each employee or director individually.
P11D(b) – Employer Summary
Declares:
-
That all P11Ds are correct
-
The total Class 1A NIC due
Employers must submit BOTH when benefits are provided.
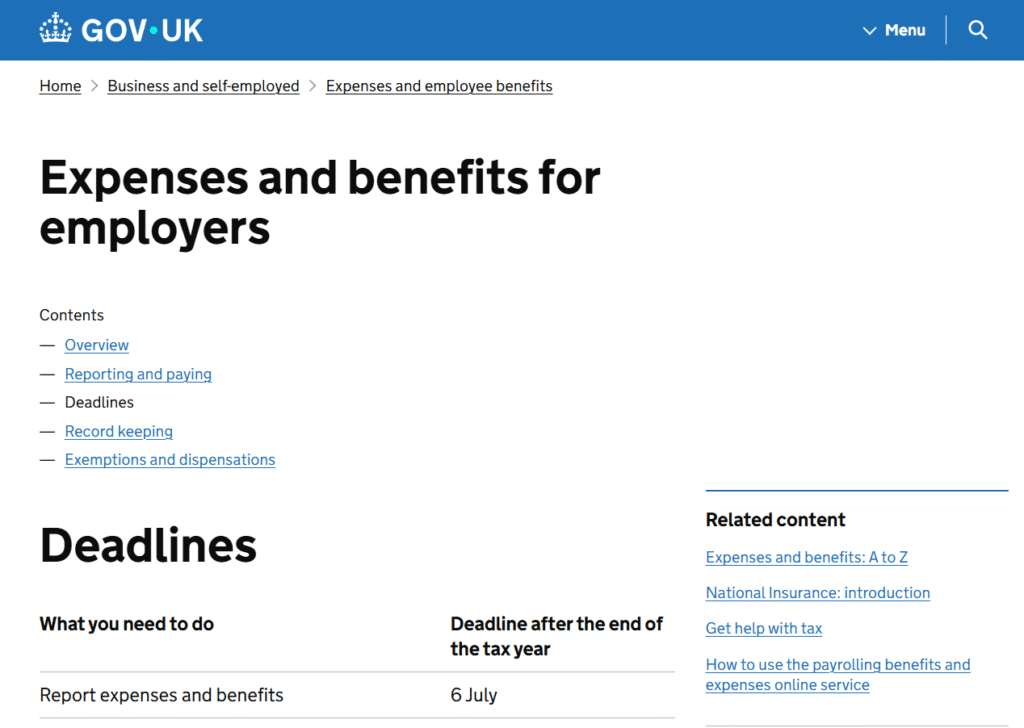
P11D Deadlines
Submission deadline:
6 July following the end of the tax year.
Class 1A NIC payment deadline:
22 July (if paying electronically)
19 July (if paying by cheque)
Late submissions → automatic penalties.
HMRC deadline information:
https://www.gov.uk/employer-reporting-expenses-benefits/deadlines
How to Submit P11D Forms
HMRC requires P11Ds to be filed online through one of the following:
-
HMRC PAYE Online
-
Commercial payroll software
-
HMRC interactive PDF
-
Payroll agents using professional software
Paper P11Ds are no longer accepted unless you have a digital exemption.
Understanding Class 1A National Insurance
Class 1A NIC is an employer-only National Insurance charge on taxable benefits.
Rate:
13.8% (2024/25)
Class 1A NIC is calculated based on:
-
The taxable value of all benefits
-
Payrolled benefits AND non-payrolled benefits
Payment reference must include your Accounts Office reference + “2313” (or applicable tax year indicator).
How to Complete the P11D (Step-by-Step)
Below is a practical guide for each section.
A – Assets Transferred
Covers:
-
Company equipment given permanently to an employee
-
Market value minus payments made by the employee
B – Payments Made on Employee’s Behalf
Employer-paid:
-
Bills
-
Fees
-
Personal liabilities
All must be reported unless fully reimbursed.
C – Vouchers & Credit Cards
Includes:
-
Retail vouchers
-
Store cards
-
Credit card purchases
D – Living Accommodation
Some accommodation is exempt if job-related (e.g., caretakers).
E – Mileage, Travelling & Subsistence
If reimbursed above HMRC approved mileage rates:
https://www.gov.uk/expenses-and-benefits-business-travel-mileage
The excess is taxable.
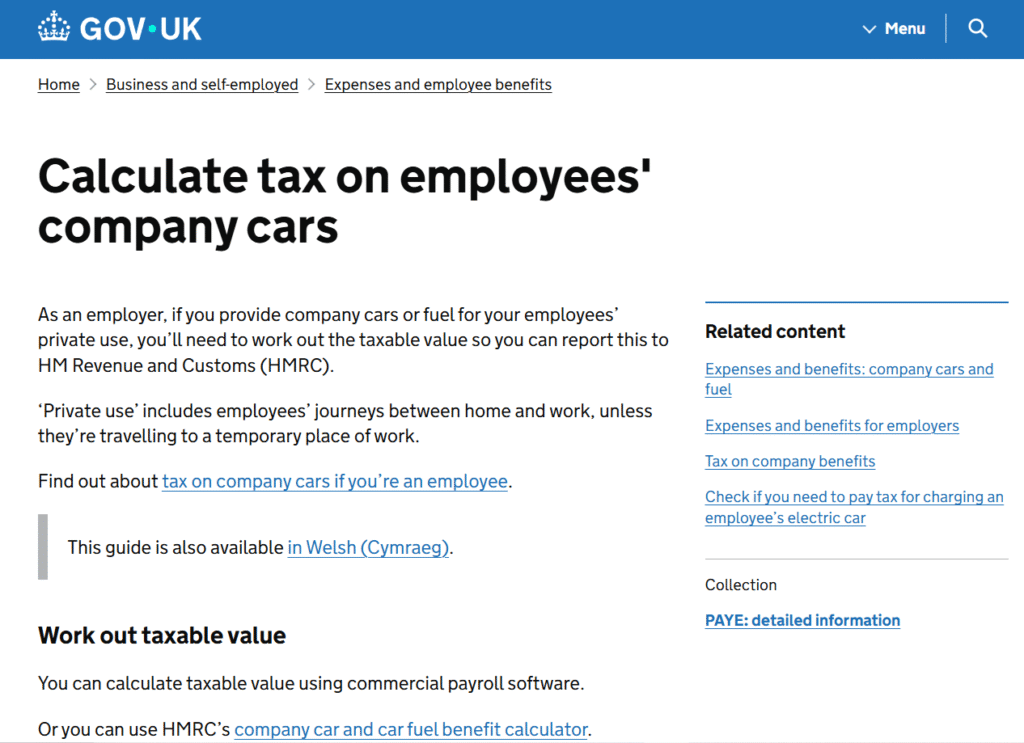
F – Cars & Car Fuel
Based on:
-
Car list price
-
CO₂ emissions
-
Fuel type
-
Employee contributions
HMRC car benefit calculator:
https://www.gov.uk/calculate-tax-on-company-cars
G – Vans & Fuel
Van benefit applies only if the van is used privately.
H – Interest-Free or Low-Interest Loans
Report if loans exceed £10,000 at any time in the year.
I – Private Medical Treatment or Insurance
Medical insurance is almost always a taxable benefit.
J – Qualifying Relocation Payments
Only the first £8,000 is exempt.
Above this → taxable.
K – Services Provided to Employee
Example:
-
Company accountants doing employee’s personal tax return
-
Personal use of corporate services
L – Assets Made Available for Use
Includes:
-
Company car not covered in Section F
-
Equipment
-
Holiday homes
-
Boats or leisure assets
M – Other Items
Covers:
-
Gifts
-
Gym memberships
-
School fees
-
Employer-provided goods
Who Pays the Tax on P11D Benefits?
Employee pays the income tax
Through PAYE tax code adjustment or Self Assessment.
Employer pays Class 1A NIC
On the taxable value of benefits.
Can P11D Benefits Be Added to Payroll? (Payrolling Benefits)
Yes — employers may choose payrolling benefits, meaning benefits are taxed automatically through payroll.
However:
-
You MUST register with HMRC via the online service before the tax year begins
-
Car and accommodation benefits have special rules
If benefits are payrolled, P11D forms are not needed (except for certain cases).
Correcting P11D Mistakes
Corrections are done via:
-
Amended P11D submission
-
Updated P11D(b)
-
Adjusted Class 1A NIC payment
-
PAYE coding corrections
Common errors:
-
Wrong car details
-
Missing benefits
-
Misclassified expenses
-
Incorrect employee payments
-
Duplicate reporting
-
Exempt items incorrectly reported
We help correct P11Ds and respond to HMRC inquiries.
Penalties for Late or Incorrect P11Ds
HMRC may issue penalties for:
Late submission
£100 per 50 employees per month.
Incorrect information
Penalties vary depending on behaviour:
-
Careless
-
Deliberate
-
Deliberate and concealed
Late Class 1A NIC
Interest + penalties apply.
PAYE Audits and HMRC Compliance Checks
HMRC monitors:
-
P11D accuracy
-
Proper use of exemptions
-
Correct valuation of benefits
-
Loan usage
-
Company car records
-
Accommodation rules
If HMRC selects your business for a PAYE audit, we act on your behalf.
HMRC guidance:
https://www.gov.uk/hmrc-internal-manuals/employment-income-manual
Case Studies
Case Study 1 – Incorrect Company Car Benefit
Employer used incorrect CO₂ data.
Tax underpaid for 3 years.
Outcome: We recalculated benefits, submitted corrected P11Ds, negotiated reduced penalties.
Case Study 2 – Unreported Medical Insurance
A firm forgot to report private healthcare for directors.
Outcome: We prepared P11Ds and P11D(b), corrected payroll, and handled HMRC correspondence.
Case Study 3 – Beneficial Loan Misreporting
Interest-free loan exceeded £10,000.
We recalculated the correct taxable benefit and filed updated P11Ds.
Case Study 4 – PAYE Audit Support
HMRC questioned travel expenses.
We provided evidence, corrected minor errors, and avoided penalties.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Who needs a P11D?
Employees or directors receiving taxable benefits.
Q2: Do I need to submit a P11D if benefits are payrolled?
Usually no — except for exempt or special cases.
Q3: What is the P11D(b)?
The employer declaration summarising Class 1A NIC due.
Q4: What happens if I submit late?
HMRC penalties apply.
Q5: Can employees claim tax relief?
Yes — in limited cases where they use benefits for work purposes.
Q6: What if the employer makes a mistake?
A corrected P11D must be submitted.
Q7: When is the deadline?
6 July each year.
Official GOV.UK guidance:
https://www.gov.uk/employer-reporting-expenses-benefits
P11D Form Preparation & Submission Services Cost UK
Prepare and submit P11D HMRC forms in the UK with professional support. We help employers report benefits and expenses accurately and on time. Our fixed-price P11D services help avoid HMRC penalties and ensure compliance.
Service Cost Estimation
Select the service category below to calculate the estimated cost of either accounting & tax services or forms and submissions.
Select Required Services / Forms
Select one or more services/forms to receive an accurate cost estimate. You can adjust your selection at any stage.
How would you like to engage our services?
Please select whether you require a one-off service or ongoing monthly support.
Contract Duration
Your cost estimate
Apply now and get 10% OFF
Submit your request today and receive an exclusive 10% discount on your selected service.
All prices are estimates. To receive a personalised quote, please fill out the form or contact us.
Ready to get started?
Get professional support from experienced UK accountants